- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
Product name : Thermoelectric Semiconductor Cooling System Cold Plate Cooler
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||
NO. | ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
1 | Material | Aluminum alloy 3003, 6063,6061 |
2 | Dimension (L*W*T) | Up to 500*500*15 mm |
3 | Cooling Capacity | 500 to 1500 W |
4 | Working Pressure | 3 to 4 bars |
5 | Flatness | 0.15 mm |
6 | Surface roughness | 3.2 um |
7 | Flow rate | 5 to 10 L/min |
8 | Manufacturing Method | CNC machining Plus vacuum brazing |
9 | Joining Method | Vacuum Brazing |
10 | Cooling Method | Liquid cooling |
11 | Surface Finish | Mill finish or anodization |
12 | Coolant | Deionized Water,Inhibited Glycol and Water,Dielectric fluid |
13 | Warranty time | 1 year |
14 | Place of Region | Jiangsu province of China |
15 | Reference Standard | GB/T 3190-2008,GB/T 14846-2008,ISO 2768 |
![]()
Cooling plates find applications in various fields like electronics, automotive, and aerospace to effectively disperse heat and avoid excessive heating.
A specific kind of cooling plate is known as a liquid-cooled plate. These plates possess channels that facilitate the flow of liquid, which absorbs heat from the surface of the plate. Subsequently, the liquid is directed to a heat exchanger, where the heat is transferred to the nearby air or water. Although liquid-cooled plates excel at dissipating substantial quantities of heat, they necessitate supplementary components like pumps and heat exchangers.
Another type of cooling plate is an air-cooled plate. This type of plate uses fins or other protrusions to increase the surface area of the plate, allowing air to flow over it and dissipate heat. Air-cooled plates are simpler in design and do not require additional components, but they may not be as efficient at dissipating heat as liquid-cooled plates.
There are also hybrid cooling plates that combine both liquid and air cooling technologies. These plates have channels for liquid flow and fins for air flow, providing the benefits of both types of cooling.

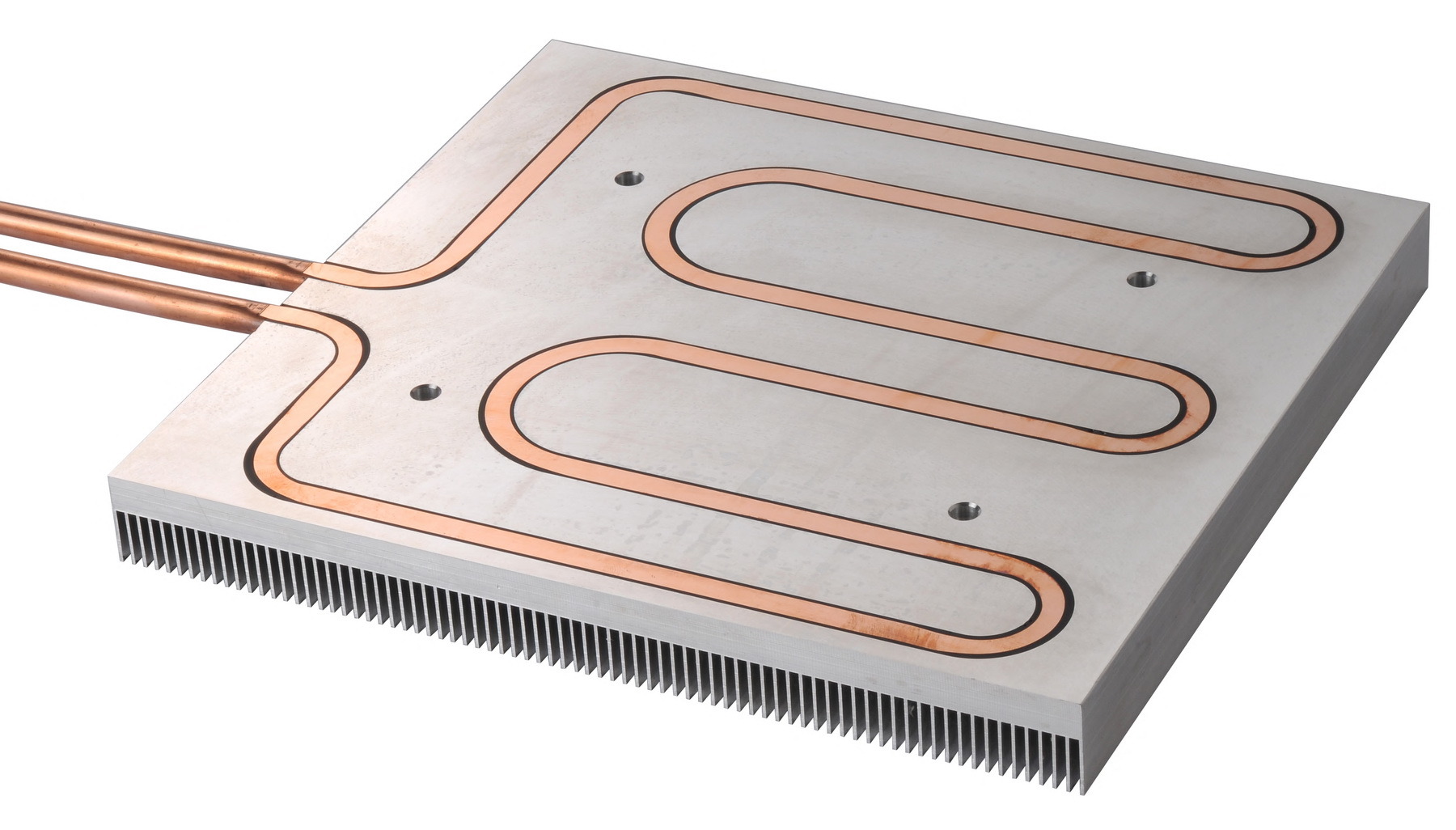
▲ Stamped and vacuum brazed cold plate ▲ Copper tubed cold plate
We also offer valuable additional components, including:
- Connectors and couplings
- Pipes and hoses
- Heat exchangers or radiators
- Tanks and pumps
- Fans
- Other accessories
The manufacturing of cooling plates utilizes various methods, such as 3D printing using additive manufacturing and traditional techniques like CNC machining. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of intricate designs and customization, while traditional methods enable cost-effective mass production of parts.

Cooling plates play a vital role in preventing overheating in various industries. There are different kinds of cooling plates and technologies available, each with their own advantages and limitations. The choice of cooling plate type and technology will depend on the specific application and requirements.
Product Applications
Product name : Thermoelectric Semiconductor Cooling System Cold Plate Cooler
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION | ||
NO. | ITEM | DESCRIPTION |
1 | Material | Aluminum alloy 3003, 6063,6061 |
2 | Dimension (L*W*T) | Up to 500*500*15 mm |
3 | Cooling Capacity | 500 to 1500 W |
4 | Working Pressure | 3 to 4 bars |
5 | Flatness | 0.15 mm |
6 | Surface roughness | 3.2 um |
7 | Flow rate | 5 to 10 L/min |
8 | Manufacturing Method | CNC machining Plus vacuum brazing |
9 | Joining Method | Vacuum Brazing |
10 | Cooling Method | Liquid cooling |
11 | Surface Finish | Mill finish or anodization |
12 | Coolant | Deionized Water,Inhibited Glycol and Water,Dielectric fluid |
13 | Warranty time | 1 year |
14 | Place of Region | Jiangsu province of China |
15 | Reference Standard | GB/T 3190-2008,GB/T 14846-2008,ISO 2768 |
![]()
Cooling plates find applications in various fields like electronics, automotive, and aerospace to effectively disperse heat and avoid excessive heating.
A specific kind of cooling plate is known as a liquid-cooled plate. These plates possess channels that facilitate the flow of liquid, which absorbs heat from the surface of the plate. Subsequently, the liquid is directed to a heat exchanger, where the heat is transferred to the nearby air or water. Although liquid-cooled plates excel at dissipating substantial quantities of heat, they necessitate supplementary components like pumps and heat exchangers.
Another type of cooling plate is an air-cooled plate. This type of plate uses fins or other protrusions to increase the surface area of the plate, allowing air to flow over it and dissipate heat. Air-cooled plates are simpler in design and do not require additional components, but they may not be as efficient at dissipating heat as liquid-cooled plates.
There are also hybrid cooling plates that combine both liquid and air cooling technologies. These plates have channels for liquid flow and fins for air flow, providing the benefits of both types of cooling.


▲ Stamped and vacuum brazed cold plate ▲ Copper tubed cold plate
We also offer valuable additional components, including:
- Connectors and couplings
- Pipes and hoses
- Heat exchangers or radiators
- Tanks and pumps
- Fans
- Other accessories
The manufacturing of cooling plates utilizes various methods, such as 3D printing using additive manufacturing and traditional techniques like CNC machining. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of intricate designs and customization, while traditional methods enable cost-effective mass production of parts.

Cooling plates play a vital role in preventing overheating in various industries. There are different kinds of cooling plates and technologies available, each with their own advantages and limitations. The choice of cooling plate type and technology will depend on the specific application and requirements.
Product Applications